Index
Get the latest news right in your inbox
Qualified Trust Service Providers are those players recognized and endorsed by the most demanding national and international institutions in terms of transparency and guarantees of online transactions. The evolution of the Internet has boosted the number of remote transactions carried out every day on different websites, which has led to the approval of new regulations governing their operation.
In previous articles, we have gone into the details of Trust Services Providers (TSPs) and Trust Third Parties. Next, we will explore what they look like and what lists comprise those that are considered qualified.
What is a trust service?
The first thing to address is the definition of the concept of "trust services". This term is included in the eIDAS Regulation and refers to services provided by one entity or company to another in connection with its operations and activities.
Trust services are the creation, verification, and validation of electronic signatures, digital time stamps or the storage and processing of electronic certificates relating to transactions carried out by digital means. To be considered as such, they must comply exhaustively with the requirements of eIDAS (electronic IDentification, Authentication, and trust Services), according to article 3.16.
In order for a company to be able to use the European Union's digital trustmark in the provision of its services, it must have been thoroughly examined by various official bodies that endorse its activity.
What are Qualified Trust Service Providers (QTSPs)?
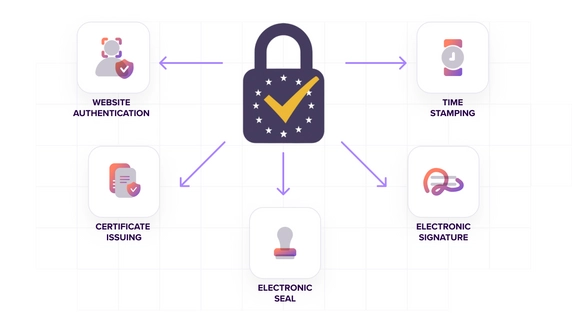
Qualified Trust Service Providers (QTSP) are those players who offer trust services under a framework endorsed by an institution capable of issuing qualified supervision. A supervisory body grants qualifications to each and every transaction carried out by these QTSPs.
Similarly, they also offer authentication services for websites, custody and preservation of digital signatures, electronic seals, and certificates that are created in the verification, authentication, and signature processes.
Digital identification is one of the most important points that concern the providers of these services, confirming that the person behind the screen before making an electronic transaction is really who he or she claims to be. For this purpose, onboarding processes are carried out with Know Your Customer standards that in real-time run hundreds of controls on the official identity documents of individuals or legal entities and on themselves (biometrics of individuals or of the UBOs of the companies to be verified - KYB).
Contracting through digital means is done completely remotely with digital signature applications thanks to qualified trust service providers, which integrate time stamps with full traceability in the audit reports of a signed document. On the other hand, electronic notifications - also included in the eIDAS regulation - are sent through QTSPs so that they have probative value in court, including options such as SMS or certified email.
Trust service platforms also offer similar functionalities to those of any document management system, but with more specific standards based on regulations such as NIS2, the RGPD, and eIDAS. The collection, processing, and custody of sensitive information such as identity documents and contracts of high-risk operations must be uploaded and stored in digital systems according to very specific requirements.
Bodies that regulate QTSPs
Each member state of the European Union has a certification body designated by the European Commission and the national government in compliance with the eIDAS regulations. In the case of Spain, for example, this is the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Digital Transformation as well as different State Secretariats of the Ministry of Industry, Trade, and Tourism (Information Society and Digital Agenda).
In most industries, having a Qualified Trust Service Provider is not only of vital importance but also a legal requirement to be able to operate in certain markets and digitally perform medium and high-risk transactions. In particular, the telecommunications industry and the BFSI areas (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) are required by law to have RegTech partners that are official QTSPs in order to offer products and services over the internet.
This provides complete and absolute legal certainty for any eventuality since the evidence collected by the QTSP will be used as evidence in any legal proceeding.
The reason why it is necessary to have a RegTech QTSP partner is that only they are qualified to offer qualified trust services, something that is required by regulation to operate and the only way to give validity and guarantees to the operations that a business carries out on the Internet. Although many players seem to offer trust services (KYC identity verification, AML controls, biometric authentication services, electronic signature contracting...) most of them are not qualified. In other words, most of the companies offering this type of service do not have the validation and backing of institutions, which invalidates the process at a legal and juridical level, even if it has been carried out in a similar technical manner.
Official lists of qualified trust services providers

Each member country of the European Union periodically publishes a list of qualified providers of trust services that includes all market players that are endorsed by their government and institutions for the issuance of qualified certificates and the offer of this type of trust services. This gives validity to electronic signatures or certificates that have been sealed through digital solutions created by these companies and their customers.
Although it may seem that there is bureaucracy about how to rely on a qualified trust service provider, the reality is quite the opposite. Thanks to the emergence of technology startups with a SaaS approach, any company can have systems based on qualified trust services in minutes. Similarly, private users can also do so by sending electronic signatures or communications on web platforms approved by the regulators that designate the QTSPs in each country.
In Spain, the official trust list of qualified providers of trust services (TSL) is public and can be consulted and downloaded through the electronic headquarters of the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Digital Transformation. In addition, free subscription models are provided so that registered users automatically receive a notification when changes occur in this list.
This list includes in parts the different types of trust services, qualified or not, offered by those players validated by the national and international institutions that oversee the eIDAS mandate:
- Service of issuance of qualified electronic certificates of electronic signature.
- Service of issuance of qualified electronic certificates of electronic seal.
- Service for issuing qualified electronic certificates for website authentication.
- Service of issuance of qualified electronic time stamps.
- Qualified certified electronic delivery service.
- Qualified service for the validation of qualified electronic signatures.
- Qualified service for validation of qualified electronic seals.
- Qualified service for the preservation of qualified electronic signatures.
- Qualified electronic seal preservation service.
- Video identification service in the issuance of qualified certificates.
- Issuance services of qualified electronic certificates of electronic seal PSD2.
- Services for issuance of qualified electronic certificates for authentication on websites using PSD2 - SCA standards.