Index
Get the latest news right in your inbox
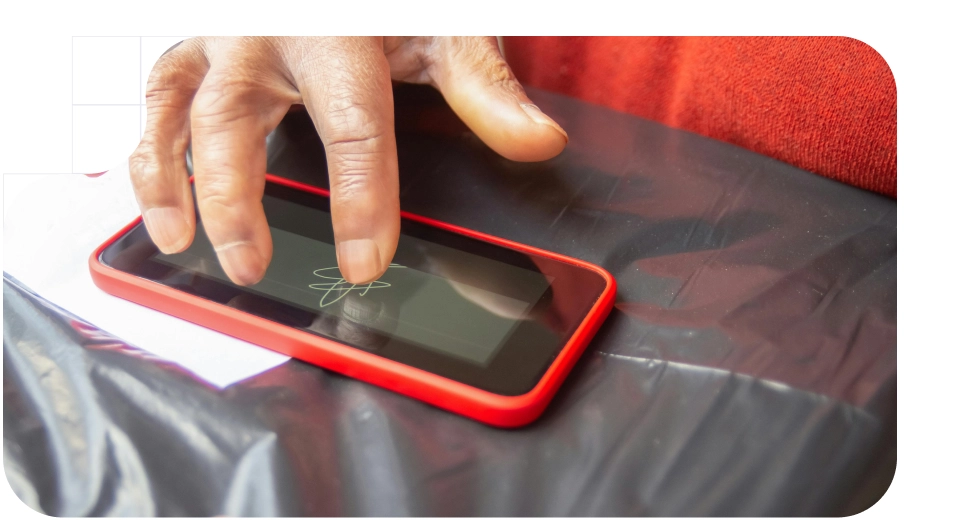
Today, in order to sign documentation through digital means, it is crucial to understand the differences between two terms that are often confused: digital signature and electronic signature. Both are important tools for authentication and security in the digital environment, but have significant differences in terms of their technology, use and legal validity.
Are they really synonymous or are they different standards that include different features and legal backing? The quick answer is: no. Electronic signatures and digital signatures cannot be used interchangeably as they have different characteristics. In this article, we will explore these differences to help you better understand which option best suits your needs.
What is a Digital Signature
Digital signature is an electronic authentication technique that uses cryptography to ensure the integrity and authenticity of a document or electronic message. That is, when we talk about Digital Signature, it is a method of encryption and decryption. After the signature of a document, a set of data is digitally added at the end, which is used to make an unequivocal identification.
It is based on public and private key technology, where a private key is used by the signer to create the digital signature, while the public key is used by the receiver to verify the authenticity of the signature. Digital signature is unique for each document or message and is uniquely and irrevocably linked to the signer.
This technology acts as a kind of "box" with a password issued by a RegTech provider validating the digital transaction. This prevents the document and the data identifying the signers and issuers of the document from being altered or modified at a later date.

Electronic Signature as a recognized standard: what is it?
Electronic signature is a legal concept that refers to any electronic method used to indicate consent or agreement to a document or electronic message by a subject (person, company...). Unlike digital signature, electronic signature does not necessarily use cryptography when it is SES for example and can include methods such as scanning a handwritten signature, the use of a biometric signature (AES), or simply writing the name on an electronic document integrating a digital certificate (QES). Electronic signature can be as simple or complex as the use case requires.
The eIDAS regulation is the norm that regulates these standards and obliges companies and users to take them into account when signing transactions according to their level of risk and the sector in which they are operating. The regulation establishes that an electronic signature is considered to be all the electronic data that accompanies information and indicates the will of one or more signatories. Therefore, in addition to digital signature, within electronic signature we find time stamps, audit documents, identity documentation, among other elements within an electronic signature process eSignature.
In addition, advanced electronic signatures (AES) contain end-to-end traceability systems that ensure non-repudiation (that the recipient of the signature request cannot deny that it was not received) and other controls to ensure integrity such as time stamps.
Digital Signature versus Electronic Signature: Which one to choose?
The techniques we have previously seen of cryptography and blockchain are the ones implemented in the case of advanced and qualified electronic signatures. In addition to these, there are many types of electronic signatures as marked by eIDAS and the additional security level added by the QTSP provider sealing the transaction.
It is important to understand that the online signature solutions that are usually offered as digital signatures are not compatible with the legal standards set by eIDAS and the regulatory bodies of the different countries. However, those considered as electronic signature by the EU do include all the standards of digital signatures in addition to those necessary to be considered in their advanced and qualified models.
Thus, we see that the main difference between a digital signature and an electronic signature is that electronic signature is 100% legal and binding - confirming an agreement between parties - while digital signature is not intended to legitimize an act of will, but simply to encrypt data to secure the content of an electronic document.
Before deciding on a digital or electronic signature tool, take into account all these aspects and ask the supplier about the legal support it can provide and the audits that the tool has passed by the regulators.


Key differences between Digital Signatures and Electronic Signatures
The eIDAS Regulation establishes a series of requirements that advanced electronic signatures and qualified electronic signatures must meet in order to have maximum legal validity and be considered as such. These requirements are based on three fundamental pillars: authentication, non-repudiation and integrity.
- Authentication: Electronic signature must be uniquely linked to the signer, so that it can be guaranteed that only one person can use it. For this purpose, different mechanisms can be used, such as the capture of biometric data, the geolocation of the signer or the information of the device from which the signature is made. In this sense, here digital signature is responsible for validating and encrypting this data together with the content of the document as part of the total, which would be the electronic signature itself.
- Non-repudiation: The identification of the signatory associated with the sending of information must be allowed, so that he/she cannot deny having received, opened, read or signed a document. In this sense, Tecalis' advanced electronic signature incorporates technologies that allow a detailed monitoring of the process.
- Integrity: The signature of the agreement must contain blockchain technology that allows any subsequent modification of the same to be detectable. Tecalis uses a public/private key system that encrypts all the documentation generated and guarantees the integrity of the data at all times by means of a Time Stamping Authority. This is another of the processes within electronic signature where digital signature plays an essential role.
Therefore, we see how electronic and digital signatures intertwine to work together to give complete security and validity to any agreement made through digital means. It impacts the following areas:
Security Level
One of the main differences between digital signatures and electronic signatures is the level of security they offer. Digital signature uses cryptography to guarantee the authenticity and integrity of the document or message, which makes it more secure and difficult to forge. This implies that digital signature deals with the technical aspect at the security level.
On the other hand, electronic signature ensures with other methods beyond cryptography that the process is being carried out in accordance with the standards set forth in the laws of the state in which the transaction is taking place.
Legal framework
Another important difference between digital signatures and electronic signatures is their legal impact. Electronic signatures are backed by specific laws and regulations that recognize their legal validity in many countries and jurisdictions. For example, in the European Union, digital signatures are regulated by the eIDAS Regulation, which establishes standards and requirements for advanced electronic signatures and qualified electronic signatures.
On the other hand, the legal validity of digital signature may vary depending on the country and local legislation. As a general rule, inserting a digital signature is the equivalent of a simple electronic signature, which is not sufficient for most operations. It is not a recognized standard.

Audit Trail Document
Electronic signature, which evidences compliance with an agreement or contract, is integrated into the main document of the agreement or contract. However, to ensure the legal validity and traceability of the actions performed on the document, an additional element is used: the audit trail, audit document or evidentiary document.
This additional document functions as a logbook that collects detailed information about each action performed on the main document in an electronic signature process, including:
- Unique transaction identifier: A code that allows each transaction to be individually and univocally identified.
- Name of signatory: The complete identification of the person who signed the document.
- Your e-mail address: A method of contact for the signatory.
- IP Address: The geographic location from which the document was signed.
- Geolocation: The precise physical location of the signer at the time of signing.
- Authentication history: A record of the different stages of the signature, such as signer authentication and signature validation.
- Chain of custody: A traceability of the document's path, from its creation to its signature and subsequent storage.
- Official time stamp: A digital stamp that certifies the exact date and time of the signature.
- Status completed: Confirmation that the signing process has been successfully completed.
- Encryption and time stamping: keys to integrity and legal validity:
All evidence of the transaction generated during the signature process is collected in the evidentiary document. Through an encryption algorithm and official time stamping that works thanks to digital signature technologies, the data integrity of the entire electronic signature is ensured, i.e. that it has not been modified since its creation. This guarantees the legal validity of the Audit Trail as irrefutable proof of who signed the document, when and where.
Technology Used
The technology used is also different in digital signatures and electronic signatures. Digital signatures use public and private key technology to create and verify the authenticity of the signature, while electronic signatures can use a variety of electronic methods, including handwritten signature scans, SMS OTP, biometric signatures, or simply typing the name on an electronic document and inserting it along with a qualified certificate. As a conclusion, all technologies used together in electronic and digital signatures revert to benefits such as:
- Increase security and confidence in electronic transactions.
- Reduce the risk of fraud and counterfeiting.
- Streamline processes and improve efficiency.
- Comply with legal and tax regulations.
About PDF conversion before esignature
An important part of the digital and electronic signature process is the conversion of documents to electronic formats such as PDF. Thanks to solutions like Tecalis, it is no longer necessary to resort to PDF conversion tools that will allow you to prepare electronic documents for digital or electronic signature. It is already integrated within this global tool, like other functionalities such as automated generation and redaction of documents with GPT technology.
Explore the different tools and techniques available to convert physical documents to PDF, edit and modify existing PDF documents can now be done directly from official tools validated by the European Union such as Tecalis, and digitally sign a PDF even if you upload a word to guarantee its authenticity and security in the digital world.
When to use Digital Signature and Electronic Signature? Aspects in common
Digital Signature
Digital signature is ideal for situations where a high level of security and authenticity is required, such as legal contracts, financial transactions, and sensitive documents that require protection against forgery and tampering. It is especially useful in business and government environments where critical documents requiring a high level of security and legal compliance are handled.
Therefore, we see how in these areas the advanced electronic signature is used, which includes all digital signature technologies in addition to a legal support similar to a notarial process.
Electronic Signature
On the other hand, electronic signatures are more suitable for situations where a quick and convenient way to indicate consent or agreement with a document or electronic message is needed. Electronic signature tools are usually complete suites where the entire contractual and document management of a business can be worked on.
It is useful in a variety of contexts and adapts to the use case by choosing the type of electronic signature and whether or not it integrates which digital signature technologies. It allows all types of contracts such as leases, service agreements, application forms, and emails that require a signature to confirm receipt or agreement with specific content.