Index
Get the latest news right in your inbox
Telecommunications industry in Chile is undergoing a radical transformation in terms of digital security and identity verification. With the entry into force of recent regulations, the country is at the forefront in the fight against fraud, identity theft and related crimes, forcing companies to incorporate KYC (Know Your Customer) processes, advanced electronic signature and biometric technologies in each procedure. This change not only strengthens the protection of users, but also boosts the modernization of the sector, generating confidence in the market and guaranteeing agile and secure processes.
The following details the current context, regulatory requirements and technological solutions that are being implemented to meet these obligations in an automated manner, as well as a guide on how to adopt these measures without friction for the end user.
Telecommunications companies in Chile
Companies operating in the telecommunications market in Chile, such as Movistar, Entel, Claro, VTR and Wom, have been forced to adapt their internal processes to the new regulations. These companies must now integrate verification methods ranging from facial recognition to fingerprint biometrics and advanced electronic signature, in order to validate the user's identity in each operation.
The telecommunications market in Chile is one of the most competitive and advanced in Latin America. Consolidated companies, both local and international, have driven the modernization of the sector through investments in infrastructure, 5G connectivity and digital services. With the mandatory incorporation of KYC technologies, electronic signature and face recognition, the need to adopt innovative solutions that meet high standards of security and efficiency is intensifying.
Telecommunications operators must now face the challenge of integrating processes that allow them to verify the identity of their customers remotely and without complications, avoiding identity theft and reducing the risk of fraud.
Face recognition, biometrics and electronic signatures in telecom
The digital transformation in the sector has led operators to invest in state-of-the-art identity verification systems. Among the technologies that have become standard, the following stand out:
- Facial recognition: Artificial intelligence-based systems allow comparing the image captured in real time with the streaming video and photograph recorded in official documents. This KYC user verification method not only speeds up the validation process, but also minimizes the possibility of fraud, as it analyzes unique facial features that are difficult to replicate through static or manipulated images.
- Advanced electronic signature: The digital signature, legally endorsed, allows the subscription of telecom contracts and other documents remotely. Thanks to its legal validity and its integration in digital platforms, companies can manage operations without the need for physical presence, reducing friction and waiting times.
The adoption of these technologies responds to the need to combat crimes such as SIM swapping, fraudulent porting and other illicit practices, while complying with regulatory requirements and improving the user experience by eliminating manual and time-consuming processes.
Subtel: new obligations and requirements
The Undersecretariat of Telecommunications (Subtel) is the entity in charge of regulating and supervising compliance with regulations in the sector. With the approval of Resolution 566 (and other complementary regulations), new parameters are established that oblige all telecommunications operators to incorporate advanced mechanisms for identity verification, electronic signature and digital security.
Requirements and obligated companies
The new regulations impose obligations on both traditional and digital telecommunications service providers. Among the requirements established are the following:
- Mandatory identity verification: Every procedure, whether it is the contracting of a new service, the modification of a contract or the activation of a portability must include a biometric verification process. This implies that the user must present his/her identity card or passport, whose data will be checked by facial recognition or by capturing his/her fingerprint.
- Implementation of advanced electronic signature: Contracts and digital documents must have a certified electronic signature. This measure ensures that, in case of discrepancies or litigation, the transaction has legal backing.
- Process automation: The regulations promote the use of automated systems that integrate biometric validation and electronic signature without manual intervention, thus reducing errors and speeding up the approval of applications.
- Safeguarding personal data: Companies are obliged to guarantee the security and privacy of their users' personal information, complying with local data protection regulations. This translates into the implementation of encryption and secure storage protocols.
In terms of scope, the regulation applies to all companies in the sector, regardless of the service channel (face-to-face, telephone or digital). The objective is to achieve "indubitable" verification of the user's identity in each transaction, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and guaranteeing a safer and more reliable service.
KYC and biometrics tools for telecommunications
The Know Your Customer (KYC) process is fundamental in the digital sphere and has become a pillar in the fight against financial and identity crimes. In the telecommunications sector, the implementation of KYC solutions makes it possible to validate the user's identity remotely and automatically, optimizing both the customer experience and the companies' internal processes.
Among the tools and solutions being adopted are the following:
- eKYC platforms: These solutions allow users to register and verify their identity by scanning official documents (such as ID cards, passports or driver's licenses) and biometric validation through facial recognition. Specialized companies offer APIs that integrate directly into the digital onboarding flow, drastically reducing approval times.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems: The combination of different verification methods (document, facial and fingerprint) enhances security and reduces the risk of identity theft. Requiring more than one verification factor makes it much more difficult for cybercriminals.
- Integration with official databases: To ensure the authenticity of documents, many KYC solutions integrate with databases of the Civil Registry and other government entities. This allows real-time validation that the information provided matches the officially registered information.
- Digital signature solutions: In addition to the verification process, the advanced electronic signature is integrated into the same platform, allowing the signing of contracts and agreements digitally. This translates into a comprehensive process that covers from identity validation to the formalization of legal agreements.
These tools not only comply with current regulations, but also offer significant benefits, such as reduced operating costs, improved user experience and accelerated contracting and customer service processes.

Electronic signature in telecommunications contracts
The advanced electronic signature has become an indispensable element in the digitalization of commercial and contractual processes. In the context of telecommunications, its use is mandatory to formalize contracts, modifications and any agreement that requires legal backing.
- Agility in contract management:
Electronic signatures allow contracts to be formalized instantly, eliminating the need to print, sign and scan documents. This not only speeds up the process, but also facilitates the storage and retrieval of information. - Legal security:
Electronic signatures have a solid legal framework to support them. In Chile, the regulations recognize the validity and authenticity of these mechanisms, which gives confidence to users and guarantees the integrity of contracts. - Reduction of errors and fraud:
By integrating with secure digital systems, electronic signatures minimize the risk of document tampering and alterations. In addition, the linkage with KYC and biometrics systems adds an additional layer of verification, making the possibility of fraud virtually nil. - Sustainability and paper reduction:
The digitization of contracts contributes to a sustainability policy, reducing the use of paper and the costs associated with logistics and physical storage of documents.
The implementation of electronic signatures in telecommunications is a comprehensive solution that meets both the needs of the sector and the demands of an increasingly digital and globalized market.
How to implement the best solutions in an affordable and frictionless way for users
The integration of advanced technologies into the identity verification process must be done in a way that is frictionless for users. The key is to balance security with user experience by implementing solutions that are intuitive, fast and efficient. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
1. Evaluation and selection of technology suppliers
Before implementing any solution, it is essential to conduct a thorough evaluation of the suppliers in the market. Aspects to be considered include:
- Certifications and compliance:
Ensure that platforms comply with local and international regulations (e.g., ISO standards, data protection regulations, and security certifications). - Integration and compatibility:
Solutions must be compatible with the company's current systems and allow for easy integration, minimizing implementation times and possible service interruptions. - Scalability:
It is important to choose solutions that can grow along with the business, adapting to an increase in demand without losing performance or security.
2. User-centered design
The implementation of verification tools should not interfere with the user experience. Some recommendations include:
- Intuitive and user-friendly interface:
Design registration and verification processes that are easy to use, with clear instructions and no unnecessary steps. The experience should be as seamless as possible to avoid losing potential customers. - Multi-channel support:
Provide assistance through multiple channels (online chat, help centers, telephone support) to resolve doubts or problems during the verification process. - Real-time feedback:
Implement mechanisms that inform the user about the progress of their verification, reducing anxiety and building confidence in the process.
3. Testing and continuous validation
To ensure the correct functioning of the solutions, it is vital to carry out periodic tests and collect feedback from users:
- Pilots and user testing:
Running pilot programs in controlled environments allows you to identify potential failures or friction points prior to full-scale deployment. - Analysis of metrics and KPIs:
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) related to verification success rate, response times and customer satisfaction, and make adjustments based on the results. - Constant updates and improvements:
Technology evolves rapidly, so it is essential to have a continuous upgrade plan that incorporates new functionalities and reinforces the security of the system.
Conclusions and recommendations
The mandatory implementation of KYC, electronic signature and biometrics in the telecommunications sector in Chile marks a turning point in the way identity and digital security are managed. With the supervision of Subtel (Undersecretary of Telecommunications of Chile) and the support of robust regulations, companies in the sector are called to modernize their processes, ensuring a more secure, agile and reliable user experience, with great growth results.
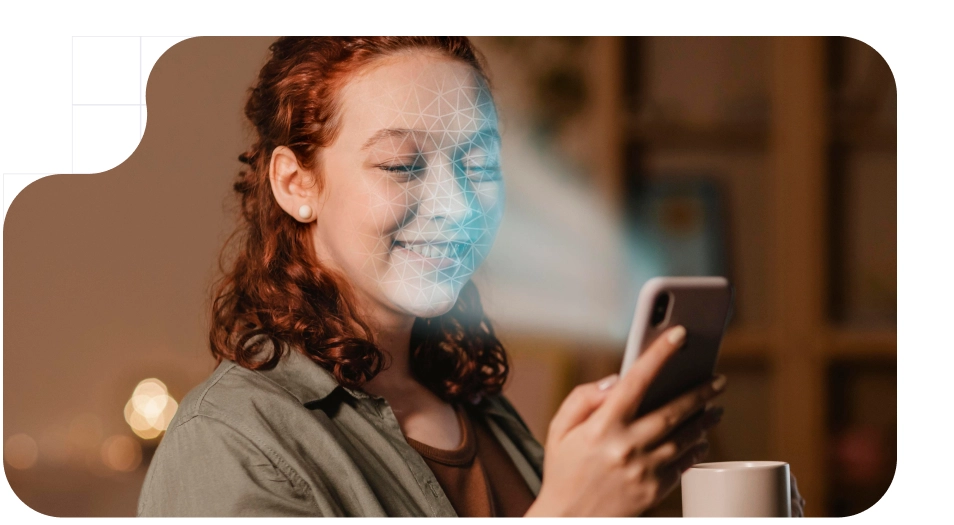

The integration of facial recognition, biometric analysis and digital signature tools not only complies with legal requirements, but also positions companies in an increasingly competitive market, where security and efficiency are key factors. By adopting these technologies, telecom not only prevent fraud and protect their customers' information, but also prepare for the future challenges of a constantly evolving digital environment and acquire more users in less time.